There are many reasons why you may want to clone a Linux partition or even hard drive, most of which are related to creating backups of your data. There are multiple ways you can achieve this in Linux by using some external tools such as partimage or Clonezilla.
However in this tutorial we are going to review Linux disk cloning with tool called dd, which is most commonly used to convert or copy files and it comes pre-installed in most Linux distributions.
How to Clone Linux Partition
With dd command you can copy entire hard drive or just a Linux partition. Lets start with cloning one of our partitions. In my case I have the following drives: /dev/sdb, /dev/sdc.. I will clone /dev/sdb1/ to /dev/sdc1.
Read Also: How to Clone Linux Partitions Using ‘cat’ Command
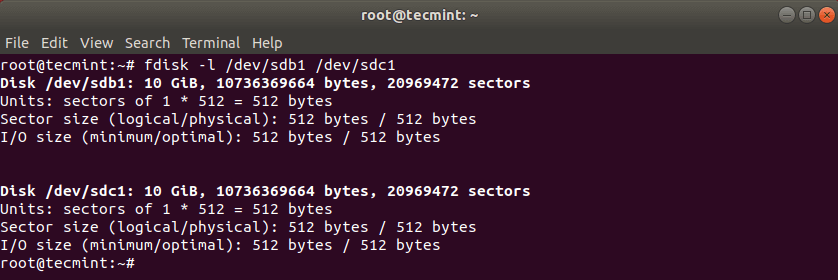
First list the these partitions using the fdisk command as shown.
# fdisk -l /dev/sdb1/ /dev/sdc1
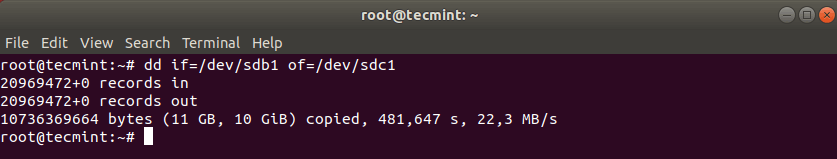
Now clone a partition /dev/sdb1/ to /dev/sdc1 using the following dd command.
# dd if=/dev/sdb1 of=/dev/sdc1
The above command tells dd to use /dev/sdb1 as input file and write it to output file /dev/sdc1.
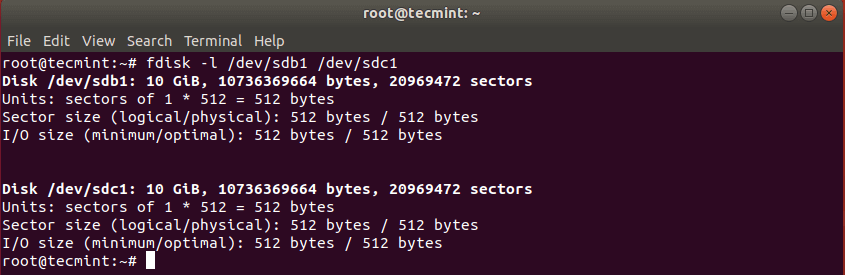
After cloning Linux partition, you can then check both partitions with:
# fdisk -l /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1
How to Clone Linux Hard Drive
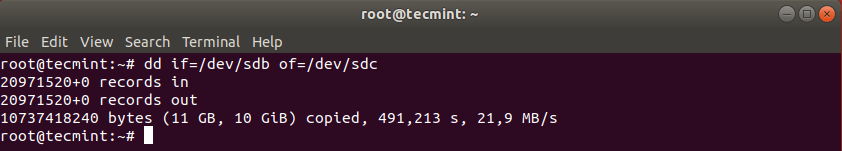
Cloning a Linux hard drive is similar to cloning a partition. However, instead of specifying the partition, you just use the entire drive. Note that in this case it is recommended that the hard drive is same in size (or bigger) than the source drive.
# dd if=/dev/sdb of=/dev/sdc
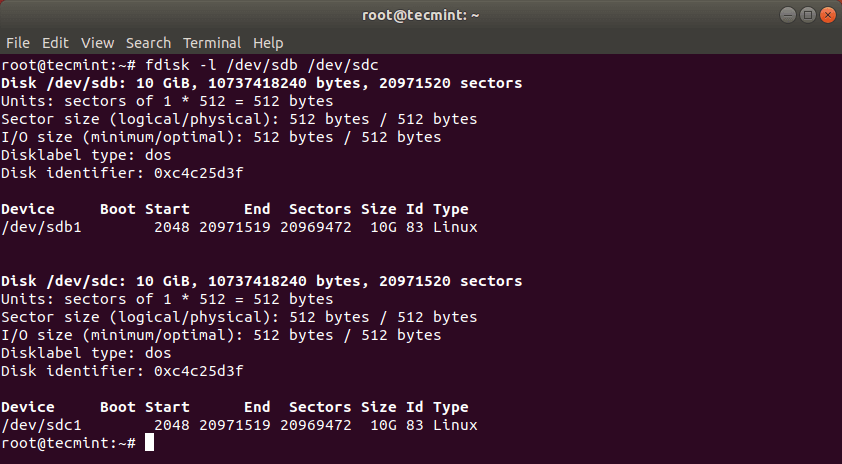
This should have copied the drive /dev/sdb with its partitions on the target hard drive /dev/sdc. You can verify the changes by listing both drives with fdisk command.
# fdisk -l /dev/sdb /dev/sdc
How to Backup MBR in Linux
dd command can also be used to backup your MBR, which is located at the first sector of the device, before the first partition. So if you want to create backup of your MBR, simply run:
# dd if=/dev/sda of=/backup/mbr.img bs=512 count=1.
The above command tells dd to copy /dev/sda to /backup/mbr.img with step of 512 bytes and the count option tells to copy only 1 block. In other words you tell dd to copy the first 512 bytes from /dev/sda to the file you have provided.
That’s all! dd command is a powerful Linux tool that should be used with caution when copying or cloning Linux partitions or drives.