In this guide, we will briefly talk about the Apache web server front-end and how to list or check which Apache modules have been enabled on your server.
Apache is built, based on the principle of modularity, this way, it enables web server administrators to add different modules to extend its primary functionalities and enhance apache performance as well.
Suggested Read: 5 Tips to Boost the Performance of Your Apache Web Server
Some of the common Apache modules include:
- mod_ssl – which offers HTTPS for Apache.
- mod_rewrite – which allows for matching url patterns with regular expressions, and perform a transparent redirect using .htaccess tricks, or apply a HTTP status code response.
- mod_security – which offers you to protect Apache against Brute Force or DDoS attacks.
- mod_status – that allows you to monitor Apache web server load and page statics.
In Linux, the apachectl or apache2ctl command is used to control Apache HTTP server interface, it is a front-end to Apache.
You can display the usage information for apache2ctl as below:
$ apache2ctl help OR $ apachectl help
Usage: /usr/sbin/httpd [-D name] [-d directory] [-f file] [-C "directive"] [-c "directive"] [-k start|restart|graceful|graceful-stop|stop] [-v] [-V] [-h] [-l] [-L] [-t] [-S] Options: -D name : define a name for use in directives -d directory : specify an alternate initial ServerRoot -f file : specify an alternate ServerConfigFile -C "directive" : process directive before reading config files -c "directive" : process directive after reading config files -e level : show startup errors of level (see LogLevel) -E file : log startup errors to file -v : show version number -V : show compile settings -h : list available command line options (this page) -l : list compiled in modules -L : list available configuration directives -t -D DUMP_VHOSTS : show parsed settings (currently only vhost settings) -S : a synonym for -t -D DUMP_VHOSTS -t -D DUMP_MODULES : show all loaded modules -M : a synonym for -t -D DUMP_MODULES -t : run syntax check for config files
apache2ctl can function in two possible modes, a Sys V init mode and pass-through mode. In the SysV init mode, apache2ctl takes simple, one-word commands in the form below:
$ apachectl command OR $ apache2ctl command
For instance, to start Apache and check its status, run these two commands with root user privileges by employing the sudo command, in case you are a normal user:
$ sudo apache2ctl start $ sudo apache2ctl status
tecmint@TecMint ~ $ sudo apache2ctl start AH00558: apache2: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using 127.0.1.1. Set the 'ServerName' directive globally to suppress this message httpd (pid 1456) already running tecmint@TecMint ~ $ sudo apache2ctl status Apache Server Status for localhost (via 127.0.0.1) Server Version: Apache/2.4.18 (Ubuntu) Server MPM: prefork Server Built: 2016-07-14T12:32:26 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Current Time: Tuesday, 15-Nov-2016 11:47:28 IST Restart Time: Tuesday, 15-Nov-2016 10:21:46 IST Parent Server Config. Generation: 2 Parent Server MPM Generation: 1 Server uptime: 1 hour 25 minutes 41 seconds Server load: 0.97 0.94 0.77 Total accesses: 2 - Total Traffic: 3 kB CPU Usage: u0 s0 cu0 cs0 .000389 requests/sec - 0 B/second - 1536 B/request 1 requests currently being processed, 4 idle workers __W__........................................................... ................................................................ ...................... Scoreboard Key: "_" Waiting for Connection, "S" Starting up, "R" Reading Request, "W" Sending Reply, "K" Keepalive (read), "D" DNS Lookup, "C" Closing connection, "L" Logging, "G" Gracefully finishing, "I" Idle cleanup of worker, "." Open slot with no current process
And when operating in pass-through mode, apache2ctl can take all the Apache arguments in the following syntax:
$ apachectl [apache-argument] $ apache2ctl [apache-argument]
All the Apache-arguments can be listed as follows:
$ apache2 help [On Debian based systems] $ httpd help [On RHEL based systems]
Check Enabled Apache Modules
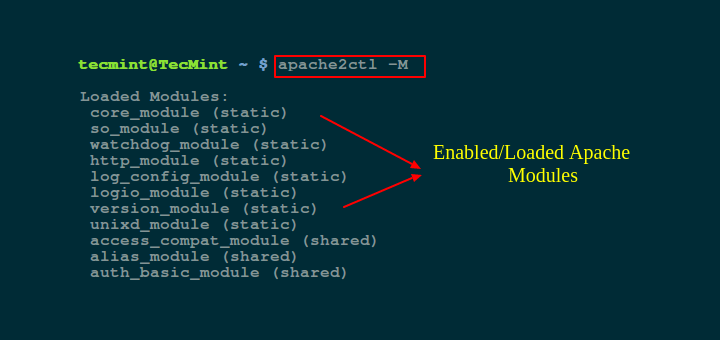
Therefore, in order to check which modules are enabled on your Apache web server, run the applicable command below for your distribution, where -t -D DUMP_MODULES is a Apache-argument to show all enabled/loaded modules:
--------------- On Debian based systems --------------- $ apache2ctl -t -D DUMP_MODULES OR $ apache2ctl -M
--------------- On RHEL based systems --------------- $ apachectl -t -D DUMP_MODULES OR $ httpd -M $ apache2ctl -M
[root@tecmint httpd]# apachectl -M Loaded Modules: core_module (static) mpm_prefork_module (static) http_module (static) so_module (static) auth_basic_module (shared) auth_digest_module (shared) authn_file_module (shared) authn_alias_module (shared) authn_anon_module (shared) authn_dbm_module (shared) authn_default_module (shared) authz_host_module (shared) authz_user_module (shared) authz_owner_module (shared) authz_groupfile_module (shared) authz_dbm_module (shared) authz_default_module (shared) ldap_module (shared) authnz_ldap_module (shared) include_module (shared) ....
That’s all! in this simple tutorial, we explained how to use the Apache front-end tools to list enabled/loaded apache modules. Keep in mind that you can get in touch using the feedback form below to send us your questions or comments concerning this guide.