Assuming you have two files or you have just created a new file and want it to have the same permissions and ownership of an older file.
In this article, we will show you how to copy permissions and ownership from one file to another file in Linux using chmod and chown commands respectively.
Copy File Permissions to Another File
To copy file permissions from one file to another file, use chmod command with the --reference switch in the following syntax, where reference_file is the file from which permissions will be copied rather than specifying mode (i.e octal or numerical mode permissions) for file.
$ chmod --reference=reference_file file
For example,
$ ls -l users.list $ ls -l keys.list $ sudo chmod --reference=users.list keys.list $ ls -l keys.list
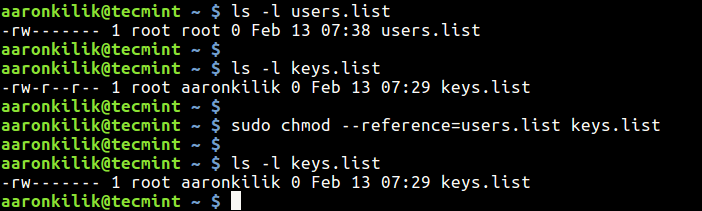
Copy File Ownership to Another File
Likewise, to copy ownership from another file, use chown command with the --reference switch as well using the following syntax, where reference_file is file from which owner and group will be copied rather than specifying owner:group values for file.
$ chown --reference=reference_file file
For example,
$ ls -l keys.list $ touch api.list $ ls -l keys.list $ sudo chown --reference=keys.list api.list $ ls -l api.list
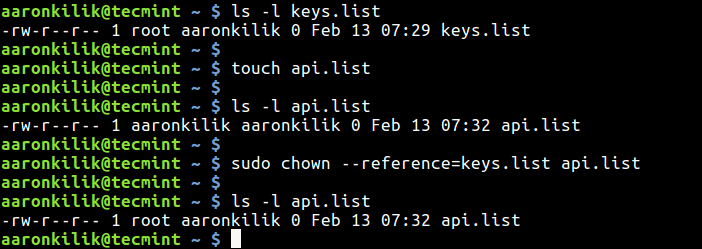
You can also copy file permissions and ownership from one file to multiple files as shown.
$ sudo chmod --reference=users.list users1.list users2.list users3.list $ sudo chown --reference=users.list users1.list users2.list users3.list
For more information, refer to the chown and chmod man pages.
$ man chown $ man chmod
You will also find these guides concerning file permissions to be useful:
- How to Manage Users and Groups in Linux
- Translate rwx Permissions into Octal Format in Linux
- How to Find Files With SUID and SGID Permissions in Linux
That’s all! If you know any other way to copy or clone file permissions in Linux, do share with us via the feedback form below.