The easiest way to count number of files and subdirectories in a directory using a tree command, which is best known for displaying files and directories in tree-like form.
Although you can always enable quotas to restrict disk space and inode usage to avoid user abuse, this command may be useful anyway. By default, the current working directory is assumed if no arguments are given:
$ tree -iLf 1
Sample Output
. ./10-Top-Linux-Distributions-of-2015.png ./adobe-flash-player-alternative.jpg ./CentOS-7-Security-Hardening-Guide.png ./coding.png ./d-logo-sketch.png ./Experts-Share-Thoughts-on-25th-Anniversary-of-the-World-Wide-Web-431806-2.jpg ./Get-Default-OS-Logo.png ./InstallCinnamonDesktoponUbuntuandFedora720x345.png ./Install-Nagios-in-CentOS.jpg ./Install-Vmware-Workstation-12-in-Linux.png ./Install-WordPress-on-CentOS-Fedora.png ./Linux-Essentials-Bundle-Course.png ./Linux-Online-Training-Courses.png ./Linux-PDF-Readers-Viewers-Tools.png ./linux-play-game.jpg ./logo.png ./nrpe-3.0.tar.gz ./Python-and-Linux-Administration-Course.png ./Ravi ./teamviewer 11 0 57095 i386 ./Telegram ./tsetup.0.10.1.tar.xz ./VBoxGuestAdditions_5.0.0.iso ./Vivaldi-About.png ./VMware-Workstation-Full-12.1.1-3770994.x86_64.bundle 3 directories, 22 files
If you want to view the same information for /var/log, do:
$ tree -iLf 1 /var/log
Sample Output
/var/log /var/log/alternatives.log /var/log/apt /var/log/aptitude /var/log/auth.log /var/log/boot.log /var/log/bootstrap.log /var/log/btmp /var/log/btmp.1 /var/log/ConsoleKit /var/log/cups /var/log/dmesg /var/log/dpkg.log /var/log/faillog /var/log/fontconfig.log /var/log/fsck /var/log/gpu-manager.log /var/log/hp /var/log/installer /var/log/kern.log /var/log/lastlog /var/log/mdm /var/log/mintsystem.log /var/log/mintsystem.timestamps /var/log/ntpstats /var/log/samba /var/log/speech-dispatcher /var/log/syslog /var/log/syslog.1 /var/log/teamviewer11 /var/log/unattended-upgrades /var/log/upstart /var/log/vbox-install.log /var/log/wtmp /var/log/wtmp.1 /var/log/Xorg.0.log /var/log/Xorg.0.log.old 13 directories, 23 files
Type the command below to view information about files and subdirectories in the directory ISOs.
$ tree -iLf 1 ISOs
Sample Output
ISOs ISOs/CentOS-6.5-x86_64-minimal.iso ISOs/CentOS-7.0-1406-x86_64-Minimal.iso ISOs/CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1503-01 ISOs/ces-standard-3.3-x86_64.iso ISOs/debian-8.1.0-amd64-CD-1.iso ISOs/kali-linux-2.0-i386 ISOs/openSUSE-13.2-DVD-x86_64.iso ISOs/rhel-server-7.0-x86_64-dvd.iso ISOs/ubuntu-14.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso ISOs/ubuntu-14.04.3-server-amd64.iso ISOs/VL-7.1-STD-FINAL.iso ISOs/Win10_1511_1_English_x32.iso ISOs/Win10_1511_1_Spanish_64.iso 2 directories, 11 files
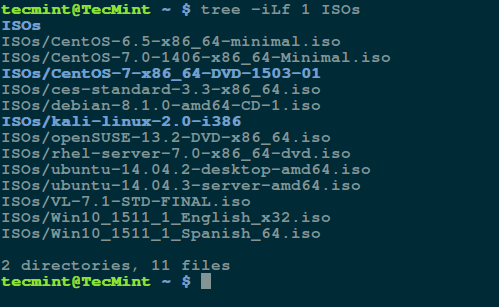
Explaining tree options used in the command above:
-i– its a graphical option that enables tree to print out indentation lines-L– specifies the level of depth of the directory tree to be displayed, which in the case above is 1-f– makes tree print the full path prefix for every file
As you can view from the image above, after listing all the files and subdirectories, tree shows you the total number of directories and files in the directory you specified.
Suggested Read: Encrypt and Decrypt Files and Directories Using Tar and OpenSSL
You can refer to the tree man page to discover more useful options, some configuration files and environment variables to better understand how it works.
Conclusion
Here, we covered an important tip that can help you use the tree utility in a different way as compared to its traditional use, for displaying files and directories in a tree-like form.
You can can build new tips by using the numerous tree options from the man page. Do you have any useful tip concerning the use of tree? Then share it with millions of Linux users around the world through the feedback form below.