The ext4 or fourth extended filesystem is a widely-used journaling file system for Linux. It was designed as a progressive revision of the ext3 file system and overcomes a number of limitations in ext3.
It has significant advantages over its predecessor such as improved design, better performance, reliability, and new features. Although it is best suited for hard drives, it can also be used on removable devices.
This article will show you how to create a new ext4 file system (partition) in Linux. We will first of all look at how to create a new partition in Linux, format it with the ext4 file system and mount it.
Note: For the purpose of this article:
- We will assume that you have added a new hard drive to your Linux machine, in which you will create the new ext4 partition, and
- If you are operating the system as an administrative user, use the sudo command to gain root privileges to run the commands shown in this article.
Creating a New Partition in Linux
List the partitions using the fdisk -l or parted -l commands to identify the hard drive you want to partition.
# fdisk -l OR # parted -l
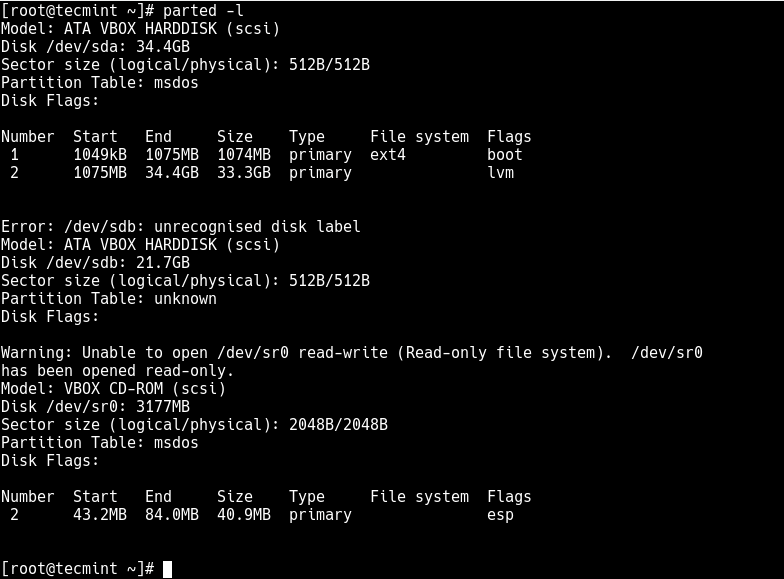
Looking at the output in the screenshot above, we have two hard disks added on the test system and we will partition disk /dev/sdb.
Now use parted command to start creating the partition on the selected storage device.
# parted /dev/sdb
Now give the new disk a label using the mklabel command.
(parted) mklabel msdos
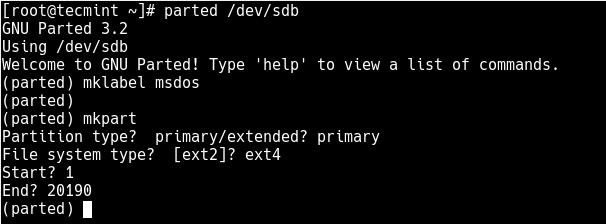
Then create a partition using the mkpart command, give it additional parameters like “primary” or “logical” depending on the partition type that you wish to create. Then select ext4 as the file system type, set the start and end to establish the size of the partition:
(parted) mkpart Partition type? primary/extended? primary File system type? [ext2]? ext4 Start? 1 End? 20190
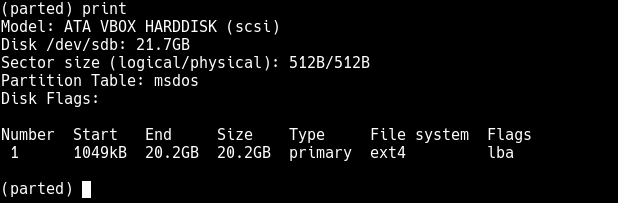
To print the partition table on the device /dev/sdb or detailed information about the new partition, run the print command.
(parted) print
Now exit the program using the quit command.
Formatting New Ext4 Partition
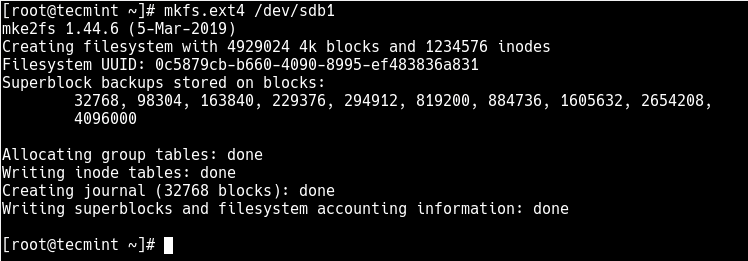
Next, you need to properly format the new partition with the ext4 file system type using the mkfs.ext4 or mke4fs command as follows.
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1 OR # mke4fs -t ext4 /dev/sdb1
Then label the partition using the e4label command as follows.
# e4label /dev/sdb1 disk2-part1 OR # e2label /dev/sdb1 disk2-part1
Mounting New Ext4 Parition in File System
Next, create a mount point and mount the newly created ext4 partition file system.
# mkdir /mnt/disk2-part1 # mount /dev/sdb1 //mnt/disk2-part1
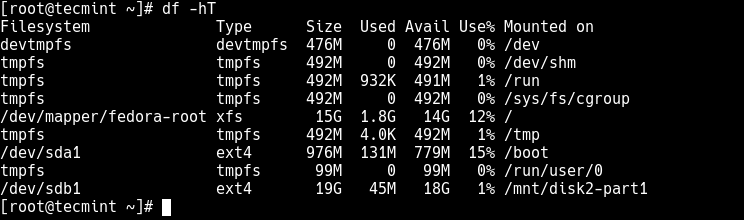
Now using the df command, you can list all file systems on your system together with their sizes in a human readable format (-h), and their mount points and file system types (-T):
# df -hT
Lastly, add the following entry in your /etc/fstab to enable persistent mounting of the file system, even after a reboot.
/dev/sdb1 /mnt/disk2-part1 ext4 defaults 0 0
You might also like to read these following related articles:
- How to Add New Disks Using LVM to an Existing Linux System
- How to Add a New Disk to an Existing Linux Server
- 10 Best File and Disk Encryption Tools for Linux
- How to Create a Virtual HardDisk Volume Using a File in Linux
That’s all! In this article, we’ve explained how to create a new partition in Linux, format it with ext4 file system type and mount it as a filesystem. For more information or to share any queries with us, use the feedback form below.