Java is one of the most popular programming languages and the JVM (Java’s virtual machine) is the run-time environment to run Java applications. These two platforms are required for much popular software that includes Tomcat, Jetty, Cassandra, Glassfish, and Jenkins.
In this article, you will learn how to install Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and the Java Developer Kit (JDK) using the default apt package manager on Ubuntu 20.04 and Ubuntu 18.04.
Installing the Default JRE in Ubuntu
The painless way for installing Java is to use the version that comes with Ubuntu repositories. By default, Ubuntu packages with OpenJDK 11, which is an open-source alternative of the JRE and JDK.
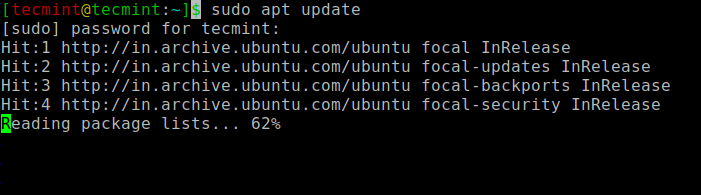
To install default Open JDK 11, first update the software package index:
$ sudo apt update
Next, check for Java installation on the system.
$ java -version
If Java is not currently installed, you will get the following output.
Command 'java' not found, but can be installed with: sudo apt install openjdk-11-jre-headless # version 11.0.10+9-0ubuntu1~20.04, or sudo apt install default-jre # version 2:1.11-72 sudo apt install openjdk-8-jre-headless # version 8u282-b08-0ubuntu1~20.04 sudo apt install openjdk-13-jre-headless # version 13.0.4+8-1~20.04 sudo apt install openjdk-14-jre-headless # version 14.0.2+12-1~20.04
Now run the following command to install the default OpenJDK 11, which will provide Java Runtime Environment (JRE).
$ sudo apt install default-jre
Once Java installed, you can verify the installation with:
$ java -version
You will get the following output:
openjdk version "11.0.10" 2021-01-19 OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 11.0.10+9-Ubuntu-0ubuntu1.20.04) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 11.0.10+9-Ubuntu-0ubuntu1.20.04, mixed mode, sharing)
Installing the Default JDK in Ubuntu
Once JRE installed, you might also need the JDK (Java Development Kit) in order to compile and run a Java-based application. To install the JDK, run the following command.
$ sudo apt install default-jdk
After installation, verify the JDK installation by checking the version as shown.
$ javac -version
You will get the following output:
javac 11.0.10
Setting the JAVA_HOME Environment Variable in Ubuntu
Most of the Java-based software programs use the JAVA_HOME environment variable to discover the Java installation location.
To set the JAVA_HOME environment variable, first, discover where Java is installed by running the following command.
$ readlink -f /usr/bin/java
You will get the following output:
/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java
Then open /etc/environment file using nano text editor:
$ sudo nano /etc/environment
Add the following line at the end of the file, make sure to replace the location of your Java installation path.
JAVA_HOME="/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64"
Save the file and reload the file to apply the changes to your current session:
$ source /etc/environment
Verify that the environment variable is set:
$ echo $JAVA_HOME
You will get the following output:
/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to install Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and the Java Developer Kit (JDK) on Ubuntu 20.04 and Ubuntu 18.04.