Awk is a powerful text processing tool that allows for efficient manipulation and extraction of information from files, particularly for handling structured data such as log files, CSV files, and more.
One of its most versatile features is the ability to print specific fields and columns from a file based on predefined delimiters.
Please refer to our previous tutorials in the Awk series.
In this article, we will explore how to leverage Awk to print fields and columns, providing practical examples and explanations to demonstrate its effectiveness.
In Awk, a “field” refers to a specific segment of text within a line, delimited by a predefined separator such as a space, tab, or comma. Each segment is assigned a field number, with the first field being $1, the second $2, and so on.
Similarly, a “column” represents a vertical grouping of fields across multiple lines. By utilizing Awk’s capabilities, we can selectively print or manipulate these fields and columns to extract valuable information from our data.
It is good to know that Awk automatically divides input lines provided to it into fields, and a field can be defined as a set of characters that are separated from other fields by an internal field separator.
If you are familiar with Unix/Linux or do bash shell programming, then you should know what the internal field separator (IFS) variable is. The default IFS in Awk are tab and space.
To understand this Awk field editing better, let us take a look at the examples below:
Use Awk to Print Fields from File
To print specific fields from a file using Awk, you can use the “print” statement along with the desired field variables.
For instance, to print the first, second, and third fields of a file separated by a comma, we can use the following command:
awk '{print $1 "," $2 "," $3}' tecmintinfo.txt
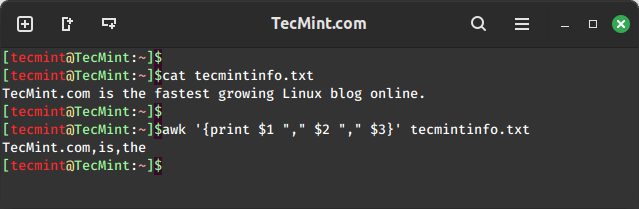
In the above command, you can see that the characters from the first three fields are printed based on the IFS defined which is space:
- Field one which is “TecMint.com” is accessed using
$1. - Field two which is “is” is accessed using
$2. - Field three which is “the” is accessed using
$3.
One important thing to note and always remember is that the use of ($) in Awk is different from its use in shell scripting.
In shell scripting, ($) is used to access the value of variables, while in Awk, ($) is used only when accessing the contents of a field, not for accessing the value of variables.
Use Awk to Print Columns from File
To print entire columns from a file, we can employ a similar approach by specifying the desired fields in the “print” statement. However, this time we consider multiple lines to collectively represent the column.
For example, to print the second and third columns of a file, we can use the following command:
awk '//{print $2, $3 }' my_shopping.txt
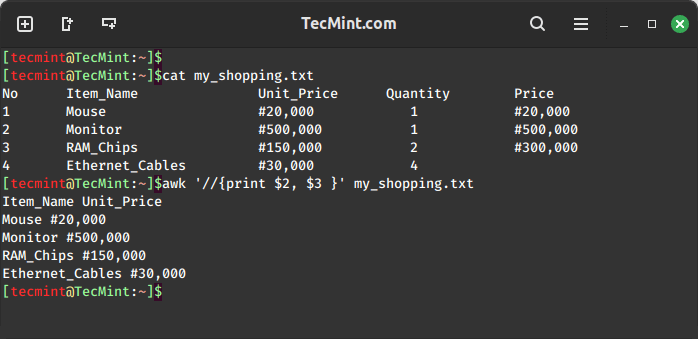
Awk also has a printf command that helps you to format your output is a nice way as you can see the above output is not clear enough.
Using printf to format the output of the Item_Name and Unit_Price:
awk '//{printf "%-10s %sn",$2, $3 }' my_shopping.txt
Use Awk to Print Field and Column Ranges from File
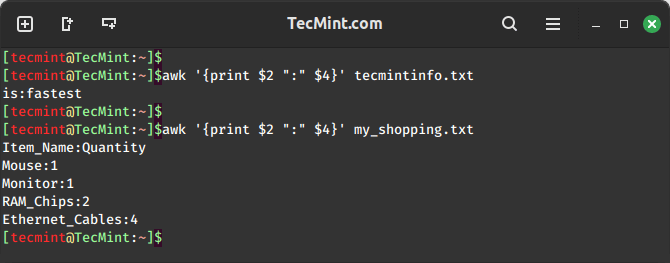
Awk also allows us to define ranges of fields or columns using the ":" operator. For instance, to print fields 2 to 4 from a file, we can use the following command.
awk '{print $2 ":" $4}' filename
Summary
Field editing is very important when using Awk to filter text or strings, it helps you get particular data in columns in a list. And always remember that the use of ($) operator in Awk is different from that in shell scripting.
I hope the article was helpful to you and for any additional information required or questions, you can post a comment in the comment section.