Are you seeking ways to efficiently handle disk partitions in Linux? In this article, we will explore some of the finest tools available to Linux users for partitioning and managing their disks.
We will cover a range of solutions, including command-line utilities and user-friendly GUI applications designed to streamline the process of disk partition management in the Linux environment.
I favor the command line over GUI (graphical user interface), I will start by describing the text-based utilities and then GUI applications as follows.
1. fdisk Command
fdisk is a versatile and widely used command-line tool that facilitates the creation and manipulation of disk partition tables, with support for various partition table formats, including MS-DOS and GPT.
fdisk provides a user-friendly, text-based, and menu-driven interface to display, create, resize, delete, modify, copy, and move partitions on disks.
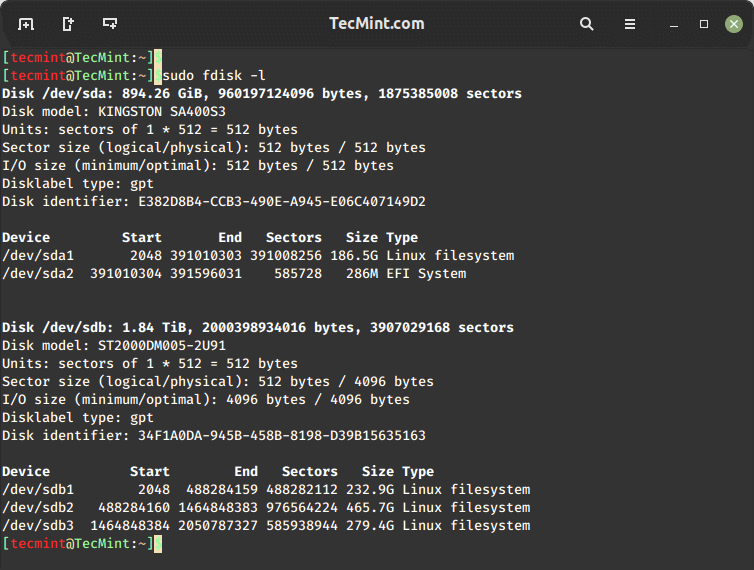
To see a list of available drives and their partitions, you can use the following command.
$ sudo fdisk -l
Next, choose the disk you want to manage.
$ sudo fdisk /dev/sda
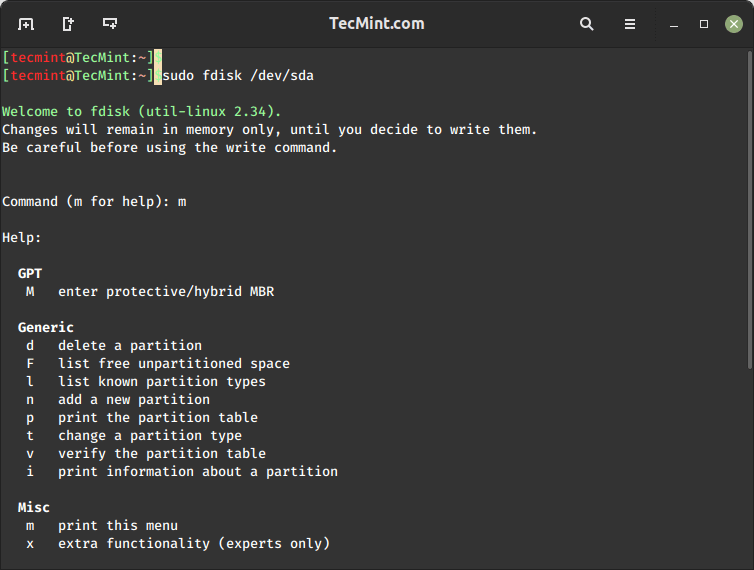
Once you’re inside fdisk, you can use the following commands to perform various partition management tasks:
p– Print the partition table to view existing partitions.n– Create a new partition.d– Delete a partition.t– Change a partition’s type.w– Save changes and exit.q– Quit without saving changes.
2. GNU Parted
Parted is a popular command line tool for efficiently managing hard disk partitions (add, delete, shrink, and extend), offering support for various partition table formats such as MS-DOS, GPT, BSD, and more.
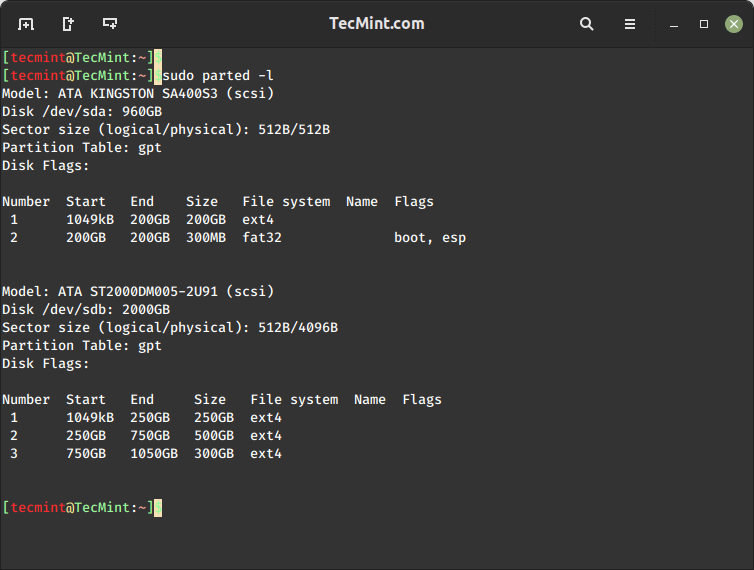
To view a list of available drives and their partitions, you can use the following command.
$ sudo parted -l
Next, select the disk you want to manage.
$ sudo parted /dev/sda
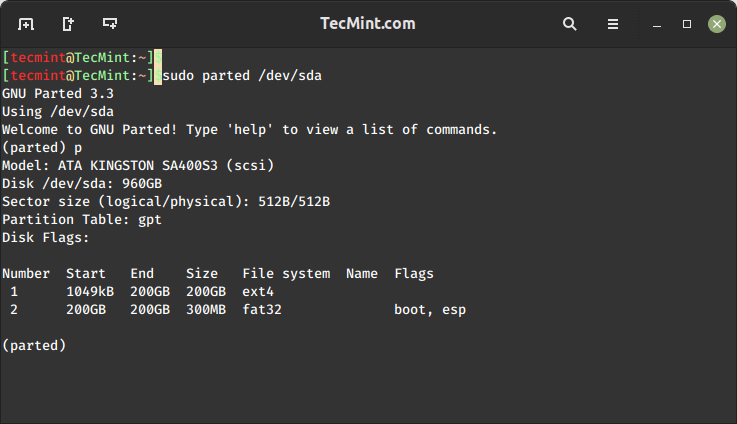
Once you’re inside parted, you can use a variety of commands to manage partitions, such as:
print– Print the partition table to view existing partitions.mkpart– Create a new partition.rm– Remove a partition.resize– Resize an existing partition.set– Set partition attributes.quit– Exit parted without saving changes.
It can also help you create space for installing new operating systems, reorganizing disk usage, and moving data to new hard disks.
3. Gparted
GParted is a free, cross-platform, and advanced graphical disk partition manager that works on Linux operating systems, Mac OS X, and Windows.
It is used to resize, copy, move, label, check, or delete partitions without data loss, enabling you to grow or shrink root partitions, create space for new operating systems, and attempt data rescue from lost partitions. It can be used to manipulate file systems including EXT2/3/4.
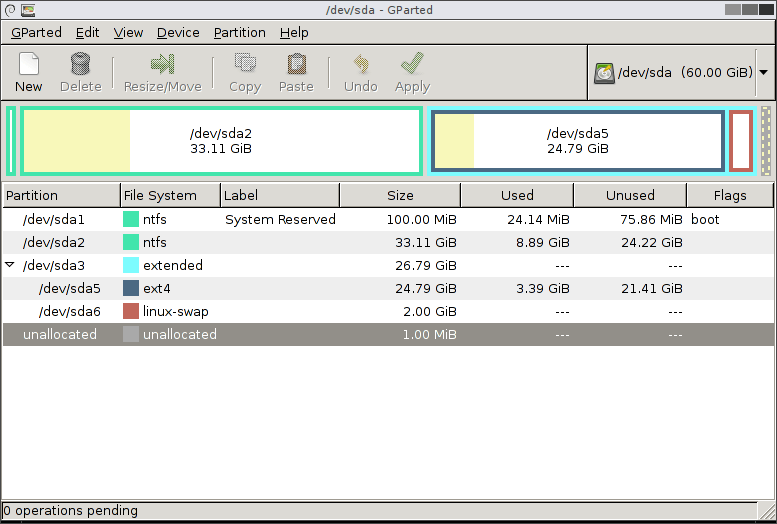
4. GNOME Disks a.k.a ( GNOME Disks Utility)
GNOME Disks is a core system utility used for disk partition management and S.M.A.R.T monitoring. It is used to format and create partitions on drives, and mount and unmount partitions. It ships with the well-known GNOME desktop environment.
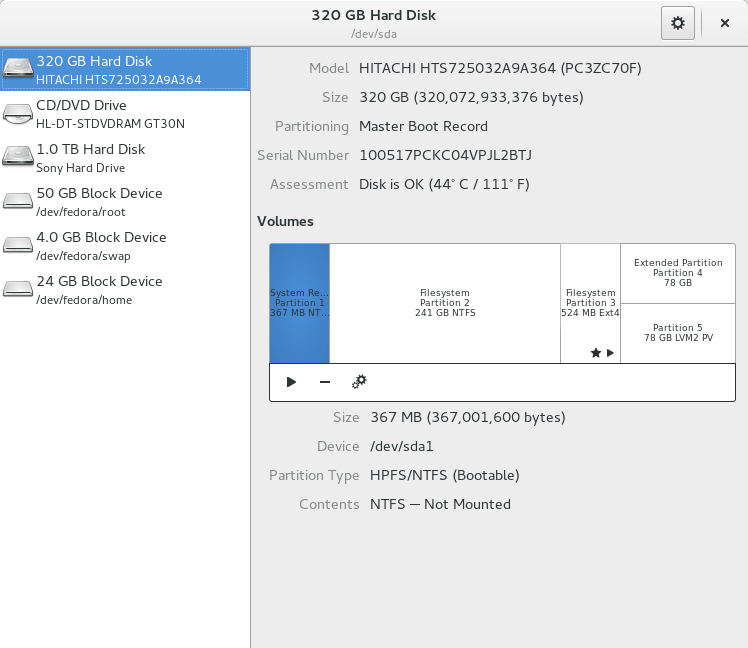
Lately, it’s been gaining features for advanced usage. The latest version (at the time of this writing) has a new feature for adding, resizing partitions, checking filesystems for any damages, and repairing them.
5. KDE Partition Manager
KDE partition manager is a useful graphical utility for managing disk devices, partitions, and file systems on your computer. It comes with the KDE desktop environment.
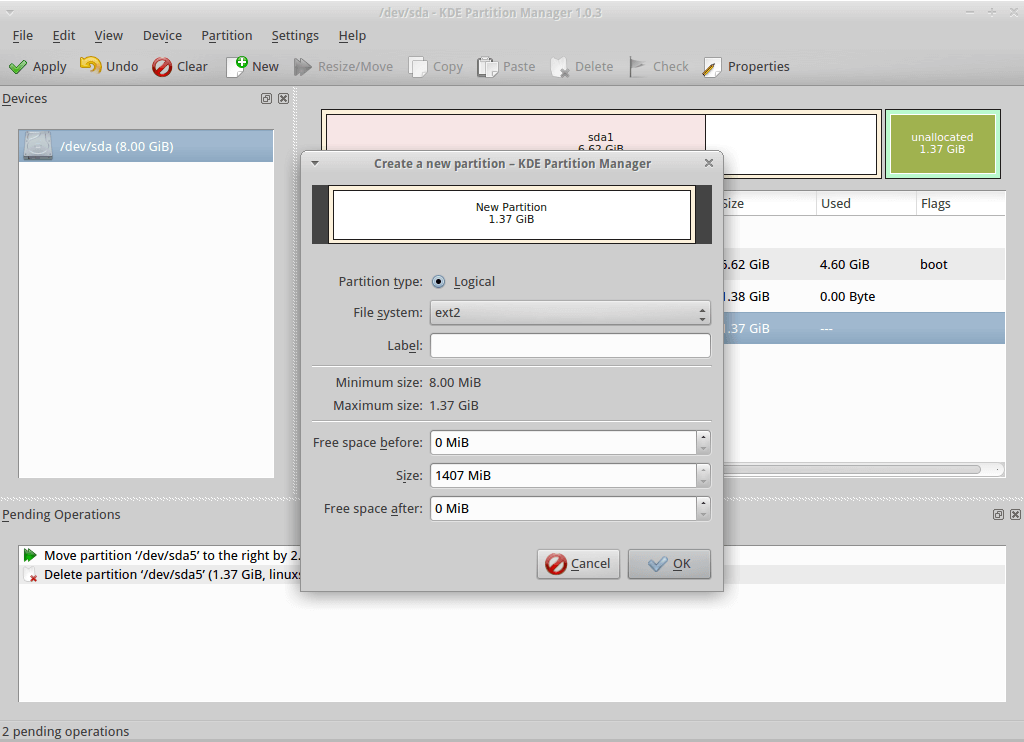
Most of its underlying work is performed by programs. It can be used to easily create, copy, move, delete, resize without losing data, backup, and restore partitions. It supports various including EXT2/3/4, BTRFS NTFS, FAT16/32, XFS, and more.
6. Qtparted
In addition, you can also use Qtparted, which is a Partition Magic (proprietary software for Windows) clone and Qt front-end to GNU Parted. Note that it is still in development and you may likely experience any kind of problem with the latest release. In that case, try to use the CVS version or a previous stable version.
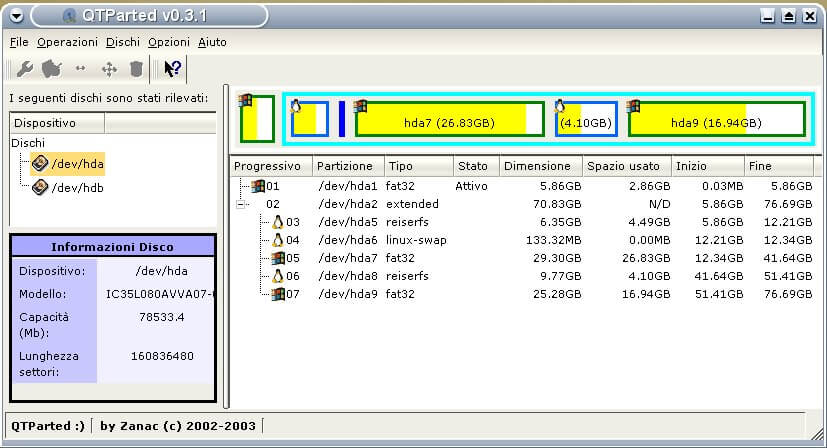
It may not be one of the best options now but you can give it a try. More features are yet to be added to it.
You might also like to read the following related articles.
These are the best partition managers and editors available for Linux operating systems. Which tool do you use? Let us know via the comment section below. Also let us know if any other partition managers for Linux, missing from the list above.