OK you might already know the most basic tips in improving WordPress blog speed which are:
a.) Using caching plug-ins
b.) Using gzip plug-ins
c.) Implementing Content delivery network (CDN)
There are a lot of tutorials on these topics found in the web. However this post would look into the less-talked approaches on how you can improve your WordPress blog loading speed. Let’s get started.
Use Google Libraries for JS framework like jQuery
Most WordPress blogs and plug-ins use jQuery framework to add JavaScript effects on the site. jQuery can reduce JavaScript coding time and make can you efficient at coding JavaScript whether you will be using it in your theme or in a plug-in.
The following are some of the causes why a JS framework like jQuery can slow down a WordPress blog:
a.) If it’s sent by the server to the user browser uncompressed. The file size is obviously bigger and takes a longer time to be loaded completely.
b.) If it’s hosted in your own server then the latency or ping is higher for those users accessing your site that is located very far from your server.
Solution: The best solution is to use Google Libraries plug-in.
This plugin would automatically change all jQuery references (or even other JS libraries such as Mootools, Prototype, etc.) from your own server to use Google hosted libraries. So instead of having a jQuery reference to the default wp-includes/js/jquery, it will be changed FROM:
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://www.php-developer.org/wp-includes/js/jquery/jquery.php?ver=1.4.2'></script>
TO:
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.7.1/jquery.min.js'></script>
If it some instances, it won’t work even after clearing the cache. Refer to the troubleshooting points:
1.) Open your theme functions.php and remove this line:
wp_enqueue_script( 'jquery' );
2.) Since you are now using Google libraries, it would be automatically replaced with:
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.7.1/jquery.min.js'></script>
This is initially found in the head section of your HTML source code.
3.) Some themes loaded their own jQuery in the head section. You can open the header.php of your template and try removing all those jQuery references (do not forget to back up your original header.php). Your objective is that there is only one jQuery line or loaded in your template.
Move JavaScript to the bottom and CSS on top
One essential technique is put all JavaScript at the bottom and leave the CSS at the top (header section). The primary reason is that JavaScript would block parallel loading of elements.
Ideally, you would put the JS files in the bottom so that it won’t interfere with the loading process. Also you should put all CSS references in the head section for efficient loading of stylesheets.
To transfer JS elements on the footer (e.g. jQuery) follow the steps below:
1.) Go to your themes functions.php.
2.) Back up your functions.php script.
3.) Open your functions.php and paste the following code in the top most part of the script.
<?php
//First remove all JS loaded in the head section
remove_action(‘wp_head’, ‘wp_print_scripts’);
remove_action(‘wp_head’, ‘wp_print_head_scripts’, 9);
remove_action(‘wp_head’, ‘wp_enqueue_scripts’, 1);
//Load JS at the footer of the template
add_action(‘wp_footer’, ‘wp_print_scripts’, 1);
add_action(‘wp_footer’, ‘wp_enqueue_scripts’, 1);
add_action(‘wp_footer’, ‘wp_print_head_scripts’, 1);?>
?>
4.) Upload or save the changes to functions.php.
5.) Reload your page. If you are using a caching plugin, you need to delete the cache and delete your browser cache/history. Reload it again.
6.) JS files like jQuery should now be located in the footer section of your template such as:
<div id="footer">
<script type='text/javascript' src='https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.7.1/jquery.min.js'></script>
</div>
Reduce Webpage Loading size and Optimize database
Even if you have cached and gzip your blog, things can still be slow if your webpage is very large in size. What makes a very large web page?
1.) Things that are loaded by WordPress in your wp_head() which are unnecessary and clutters the head section of your template.
2.) Unused references to JavaScript and plug-ins.
3.) Very large image sizes.
4.) Lots of cluttered/useless information in the WordPress MySQL database.
To solved these issues.
A.) Removing a cluttered WP Head
1.) Edit your theme functions.php script.
2.) Copy and paste the code below:
<?php
remove_action('wp_head','wp_generator');
remove_action( 'wp_head', 'feed_links_extra', 3 );
remove_action( 'wp_head', 'feed_links', 2 );
remove_action( 'wp_head', 'rsd_link' );
remove_action( 'wp_head', 'wlwmanifest_link' );
remove_action( 'wp_head', 'index_rel_link' );
remove_action( 'wp_head', 'parent_post_rel_link', 10, 0 );
remove_action( 'wp_head', 'start_post_rel_link', 10, 0 );
remove_action( 'wp_head', 'adjacent_posts_rel_link', 10, 0 );
?>
Make sure the place the above code in the top-most part of your functions.php. See screenshot below:

3.) Save the changes and upload it back to your WordPress server.
4.) Reload any of your WordPress post and see the HTML source code. You should not see anymore those not so useful dynamically generated HTML tags such as the WP meta tag generator like this:
<meta name="generator" content="WordPress 3.3.1" />
Bear in mind that if you do not see these changes because you might be using a caching plugin and you need to clear it first.
B.) Removing unused JavaScript files, etc.
Your theme might be loading some JavaScript framework but it’s not using it. To confirm by looking at the source code and examine the presence of the following JS framework. Example:
a.) Moo tools
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.yoursite.com/wp-content/themes/js/moo.js"></script>
b.) Protoype:
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://www.yoursite.com/wp-content/themes/js/prototype.js"></script>
Another tips is that you can remove unused plug-ins (delete them from your WordPress plug-in directory). You can also remove redundant plug-ins and use the WordPress built-in functionality if it is provided. A good example is the following plug-ins:
a.) Canonical URLs plugin – WordPress has a built in link rel canonical support, so it’s good to disable this to save some overheads.
b.) Wp-spamfree- WordPress has Akismet so try installing Akismet only for anti-comment spam. Another plug-in can introduce some JS or CSS in the head of your template which can slow down website loading.
2.) Duplicate jQuery loaded.
These are caused by the plugins which does not properly call jQuery in their source code resulting in duplication. You can either contact the plugin author to rewrite it or remove the duplicate jQuery loaded if you know some coding.
You can as well replace the problematic plug-in with other compatible/cleanly coded plugins.
C.) Reduce Image sizes
The standard image dimension depends also on the width of your WordPress post. However you have two methods here. Using plug-in to reduce image sizes:
Method1.) Use WP-Smush it plugin: http://wordpress.org/extend/plugins/wp-smushit/. This will reduce the image file size without dramatically reducing the quality of your WordPress post images.
Method2.) Don’t use a plugin. Instead download your entire WordPress post images to your desktop and manually convert the image file sizes to uniform/compressed sizes such as 20KB.
So in this example, if you have 80kB images, 75kb images, etc; it will all be converted to 20KB using an image processing software such as Irfanview (with RIOT plugin enabled).
The disadvantage of method 1 is that it adds additional plugin which can increase the overhead of your WordPress server (CPU and memory usage). On the other hand, the disadvantage of method 2 is that reducing all images to a uniform file sizes such as 20KB or 25KB can dramatically affect the image quality on some images.
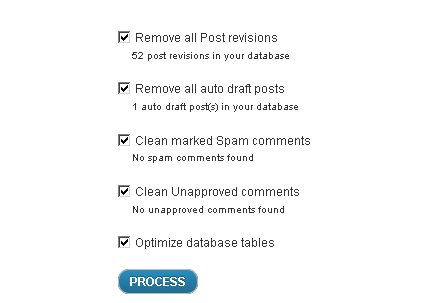
D.) Optimize WordPress MySQL database
This is really simple. Over time your MySQL database can have cluttered/useless information left by spam comments, plugin un-installation etc. These overheads can increase the size of your WordPress database and slows down your site.
The easiest solution is to use a plugin called WP-optimize.
Simply check all options and start optimizing: