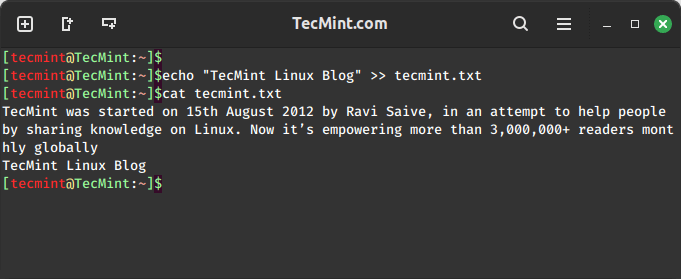
In this tutorial, I am going to take your through steps you can use to delete a user’s account together with his/her home directory on a Linux system.
To learn how to create user accounts and manage them on Linux systems, read the following articles from the links below:
- 15 “useradd” Command Examples to Manage User Accounts in Linux
- 15 “usermod” Command Examples to Change/Modify User Account Names in Linux
- How to Manage Users & Groups with File Permissions in Linux
As a System Administrator in Linux, you may have to remove users account at after sometime when a user account may become dormant for so long, or user may leave the organization or company or any other reasons.
When removing user accounts on a Linux system, it is also important to remove their home directory to free up space on the storage devices for new system users or other services.
Deleting/Removing a User Account with His/Her Home Directory
1. For demonstration purpose, first I will start by creating two user accounts on my system that is user tecmint and user linuxsay with their home directories /home/tecmint and /home/linusay respectively using adduser command.
# adduser tecmint # passwd tecmint # adduser linuxsay # passwd linuxsay
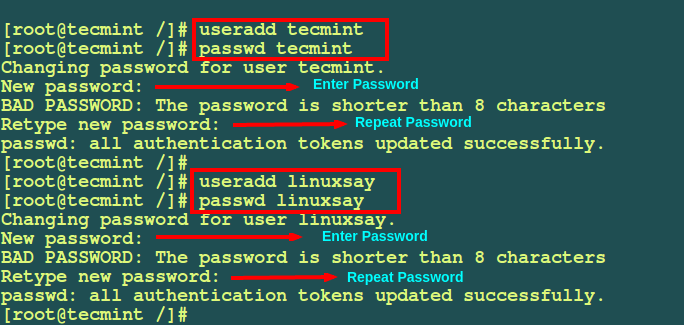
From the screenshot above, I have used the adduser command to create user accounts on Linux. You can also use useradd command, both are same and does the same job.
2. Let’s now move further to see how to delete or remove user accounts in Linux using deluser (For Debian and it’s derivatives) and userdel (For RedHat/CentOS based systems) command.
The directives inside the configuration file for deluser and userdel commands determine how this it will handle all user files and directory when you run the command.
Let us look at the configuration file for the deluser command which is /etc/deluser.conf on Debian derivatives such as Ubuntu, Kali, Mint and for RHEL/CentOS/Fedora users, you can view the /etc/login.defs files.
The values in the these configuration are default and can be changed as per your needs.
# vi /etc/deluser.conf [On Debian and its derivatives] # vi /etc/login.defs [On RedHat/CentOS based systems]
3. To delete a user with home directory, you can use the advanced way by following these steps on your Linux server machine. When users are logged on to the server, they use services and run different processes. It is important to note that user can only be deleted effectively when they are not logged on to the server.
Lock User Accounts in Linux
Start by locking the user account password so that there is no access for the user to the system. This will prevent a user from running processes on the system.
The passwd command including the –lock option can help you achieve this:
# passwd --lock tecmint Locking password for user tecmint. passwd: Success

Find and Kill All Running Processes of User
Next find out all running processes of user account and kill them by determine the PIDs (Process IDs) of processes owned by the user using:
# pgrep -u tecmint 1947 1959 2091 2094 2095 2168 2175 2179 2183 2188 2190 2202 2207 2212 2214
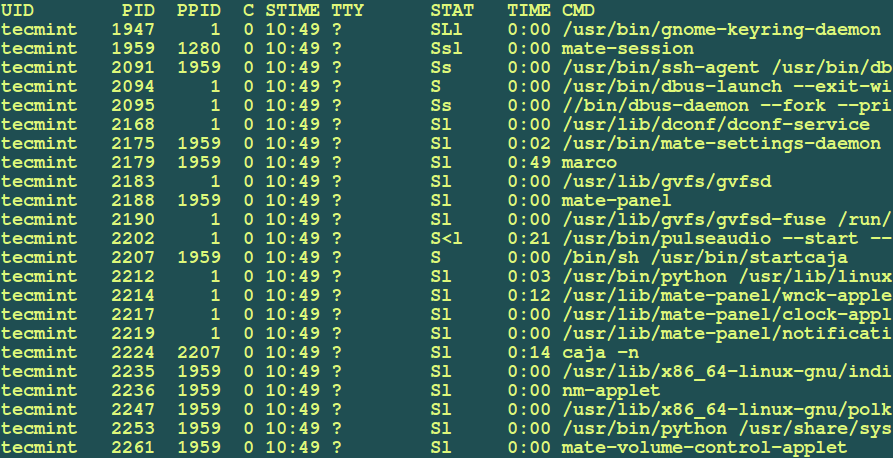
Then you can list the processes interms of username, PIDs, PPIDs (Parent Process IDs), terminal used, process state, command path in a full formatting style with the help of following command as shown:
# ps -f --pid $(pgrep -u tecmint) UID PID PPID C STIME TTY STAT TIME CMD tecmint 1947 1 0 10:49 ? SLl 0:00 /usr/bin/gnome-keyring-daemon --daemonize --login tecmint 1959 1280 0 10:49 ? Ssl 0:00 mate-session tecmint 2091 1959 0 10:49 ? Ss 0:00 /usr/bin/ssh-agent /usr/bin/dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/im-launch mate-session tecmint 2094 1 0 10:49 ? S 0:00 /usr/bin/dbus-launch --exit-with-session /usr/bin/im-launch mate-session tecmint 2095 1 0 10:49 ? Ss 0:00 //bin/dbus-daemon --fork --print-pid 6 --print-address 9 --session tecmint 2168 1 0 10:49 ? Sl 0:00 /usr/lib/dconf/dconf-service tecmint 2175 1959 0 10:49 ? Sl 0:02 /usr/bin/mate-settings-daemon tecmint 2179 1959 0 10:49 ? Sl 0:47 marco tecmint 2183 1 0 10:49 ? Sl 0:00 /usr/lib/gvfs/gvfsd tecmint 2188 1959 0 10:49 ? Sl 0:00 mate-panel tecmint 2190 1 0 10:49 ? Sl 0:00 /usr/lib/gvfs/gvfsd-fuse /run/user/1000/gvfs -f -o big_writes tecmint 2202 1 0 10:49 ? S<l 0:20 /usr/bin/pulseaudio --start --log-target=syslog tecmint 2207 1959 0 10:49 ? S 0:00 /bin/sh /usr/bin/startcaja tecmint 2212 1 0 10:49 ? Sl 0:03 /usr/bin/python /usr/lib/linuxmint/mintMenu/mintMenu.py tecmint 2214 1 0 10:49 ? Sl 0:11 /usr/lib/mate-panel/wnck-applet ....
Once you find all the running processes of user, you can use the killall command to kill those running processes as shown.
# killall -9 -u tecmint
The -9 is the signal number for the SIGKILL signal or use -KILL instead of -9 and -u defines username.
Note: In recent releases of RedHat/CentOS 7.x versions and Fedora 21+, you will get error message as:
-bash: killall: command not found
To fix such error, you need to install psmisc package as shown:
# yum install psmisc [On RedHat/CentOS 7.x] # dnf install psmisc [On Fedora 21+ versions]
Backup User Data Before Deleting
Next you can backup users files, this can be optional but it is recommended for future use when need arises to review user account details and files.
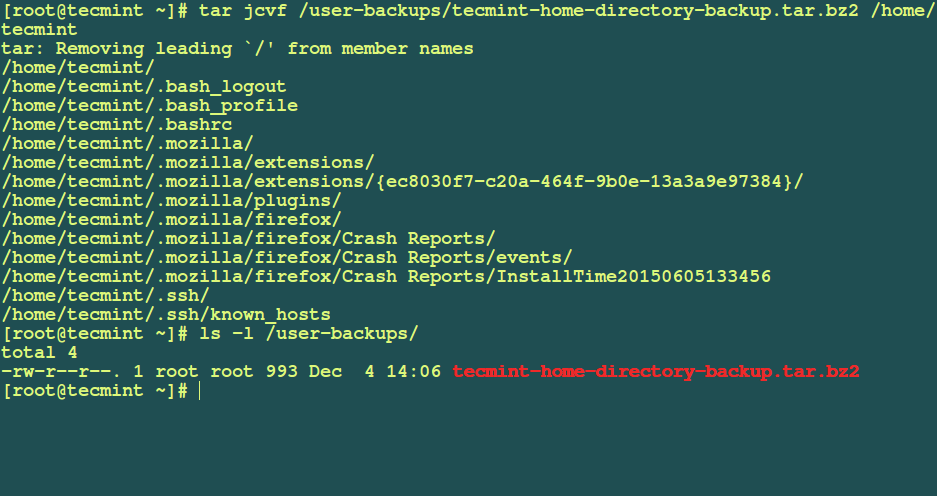
I have used the tar utilities to create a backup of users home directory as follows:
# tar jcvf /user-backups/tecmint-home-directory-backup.tar.bz2 /home/tecmint
Delete/Remove User Account and Files
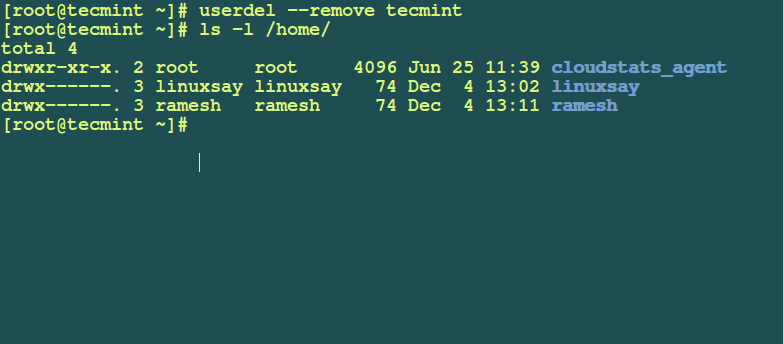
Now you can safely remove user together with his/her home directory, to remove all user files on the system use the --remove-all-files option in the command below:
# deluser --remove-home tecmint [On Debian and its derivatives] # userdel --remove tecmint [On RedHat/CentOS based systems]
Summary
That is all to do with removing user and their home directory from a Linux system. I believe the guide is easy enough to follow, but you can voice a concern or add more idea by leaving a comment.