Gitlab is an open-source, powerful, robust, scalable, secure, as well as efficient software development and collaboration platform for all stages of the DevOps lifecycle.
It allows you to plan your development process; code, and verify; package software, and release it with an in-built continuous delivery feature; automate configurations management, and monitor software performance.
It has features such as an issue tracker, moving of issues between projects, time tracking, very powerful branching tools, file locking, merge requests, custom notifications, project roadmaps, burndown charts for project and group milestones, and so much more.
Gitlab is one of the best alternatives to Github for hosting your open-source projects, which you will find out there.
In this article, we will explain how to install and configure GitLab (Git-repository manager) on RHEL-based and Debian-based distributions.
Step 1: Install and Configure Required Dependencies
1. First, start by installing the following necessary dependencies using the yum or apt package manager as shown.
sudo yum install curl policycoreutils-python-utils [On RHEL-based] sudo apt install curl policycoreutils-python-utils [On Debian-based]
2. Next, install the Postfix service to send notification emails, and enable it to start at system boot, then check if it is up and running using the following commands.
sudo yum install postfix [On RHEL-based] sudo apt install postfix [On Debian-based] sudo systemctl start postfix sudo systemctl enable postfix sudo systemctl status postfix
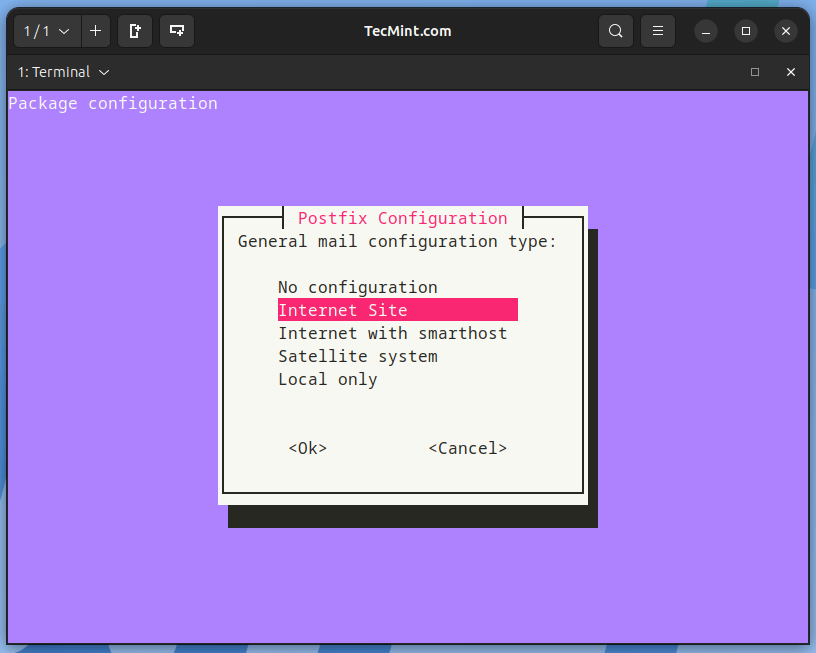
During Postfix installation a configuration window may appear. Select ‘Internet Site‘ and use your server’s external DNS for ‘mail name‘ and press enter. If extra screens appear, continue to press enter to accept the defaults.
Step 2: Add GitLab Repository and Install Package
3. Now add the GitLab package repository to your system by running the following script.
On RHEL-based systems:
curl https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ce/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash
On Debian-based systems:
curl https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ee/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
4. Next, install the GitLab Community Edition package using the following command and make sure to change ‘https://gitlab.tecmint.com‘ to the URL at which you want to access your GitLab instance from a web browser.
On RHEL-based systems:
sudo EXTERNAL_URL="https://gitlab.tecmint.com" yum install -y gitlab-ce
On Debian-based systems:
sudo EXTERNAL_URL="https://gitlab.tecmint.com" apt install -y gitlab-ee
Note: If you want to change your main URL, you can configure it in the GitLab main configuration file /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb in the external_url section. Once changed, don’t forget to reconfigure gitlab to apply the recent changes in the configuration file using the following command.
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
5. If you have a system firewall enabled, you need to open ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS) to allow connections in the system firewall.
On RHEL-based systems:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=80/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=443/tcp sudo# systemctl reload firewalld
On Debian-based systems:
sudo ufw allow http sudo ufw allow https sydo ufw reload
Step 3: Perform Initial Gitlab Setup
6. Now, open a web browser and access your gitlab instance using the following URL you set during installation.
https://gitlab.tecmint.com
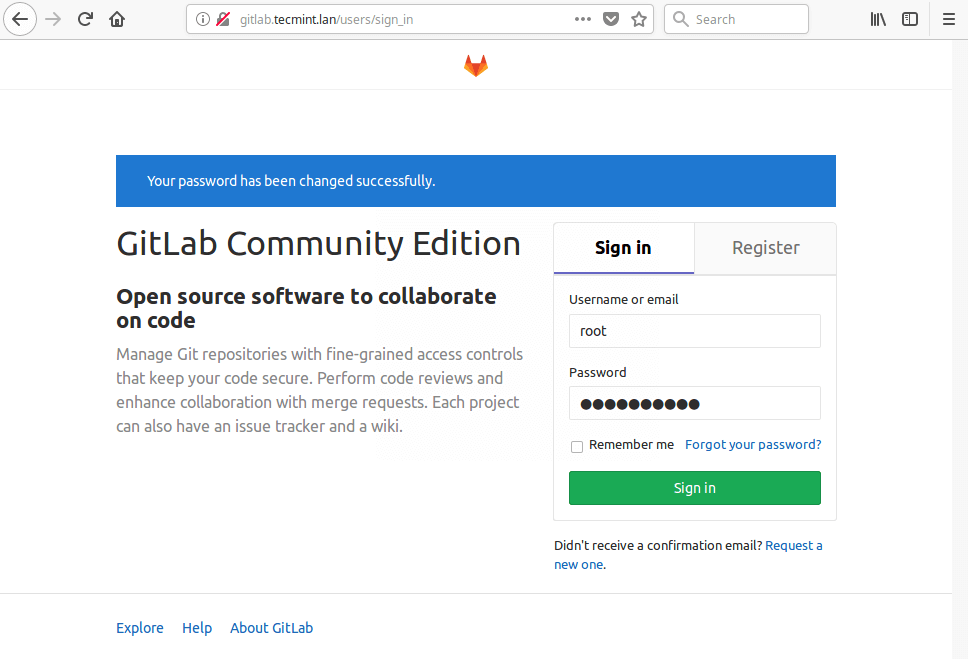
7. On your first visit, you’ll be redirected to a password reset screen, create a new password for your new admin account and click “Change your password”. Once you set it, it will be redirected back to the login screen, and log in with the username root and the password you set.
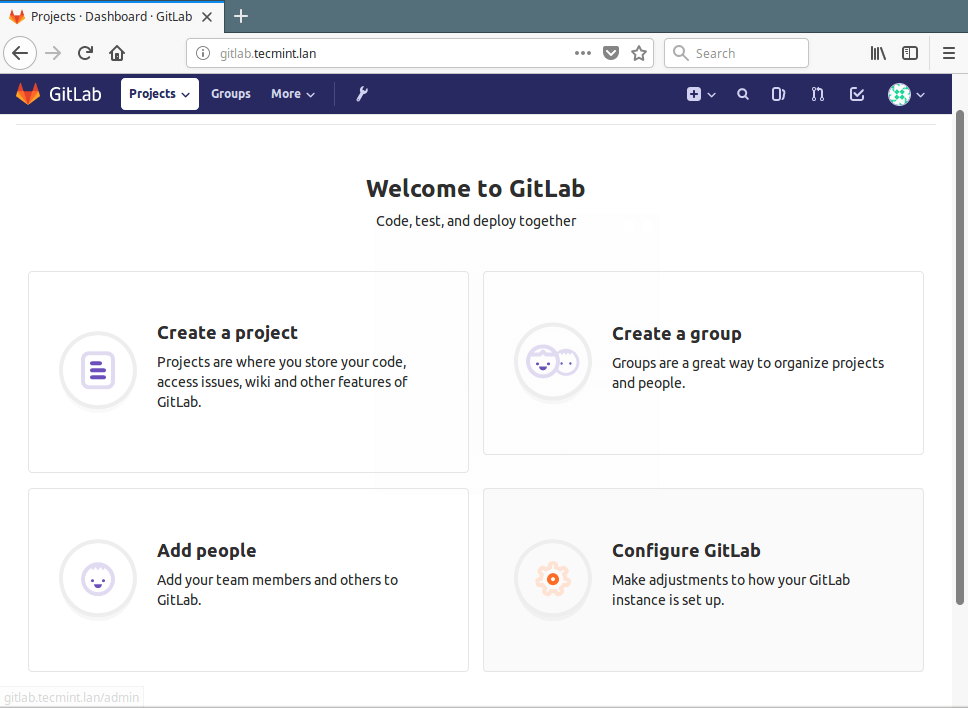
8. After a successful login, it should take you to the admin user account as shown in the screenshot. From, here, you can create an object, create a group, add people, or configure your gitlab instance as you wish. You can also edit your user profile, configure your email, add SSH keys to your gitlab instance, and more.
For more information, go to Gitlab About Page: https://about.gitlab.com/
That’s all for now! In this article, we have explained how to install and configure a Gitlab (Git-repository manager) on RHEL-based and Debian-based Linux distributions. If you have any questions or thoughts to add to this guide, use the comment form below to reach us.