PostgreSQL is a powerful, widely-used, open-source, multi-platform, and advanced object-relational database system known for its proven architecture, reliability, data integrity, robust feature set, and extensibility.
pgAdmin is an advanced, open-source, full-featured, and web-based administration and management tool for the PostgreSQL database server.
In this article, you will learn how to install the PostgreSQL 12 database server and pgAdmin 4 in CentOS 8 Linux distribution.
Step 1: Installing PostgreSQL on CentOS 8
1. First, disable the built-in PostgreSQL module by running the following dnf command.
# dnf -qy module disable postgresql
2. Next, enable the official PostgreSQL Yum Repository as shown.
# dnf install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-8-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm
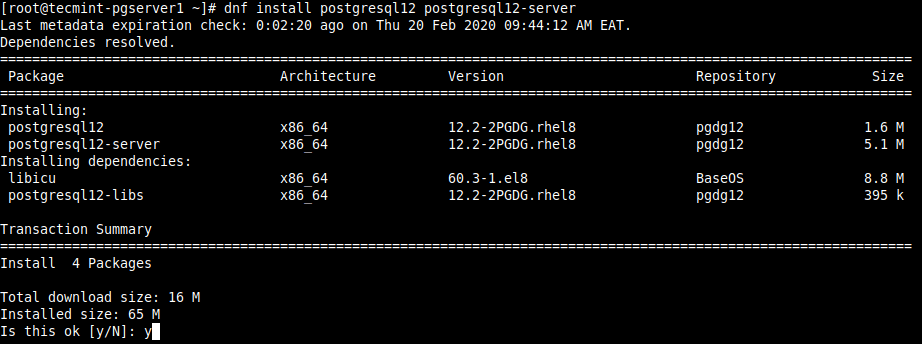
3. Next, install the PostgreSQL 12 server and client packages.
# dnf install postgresql12 postgresql12-server
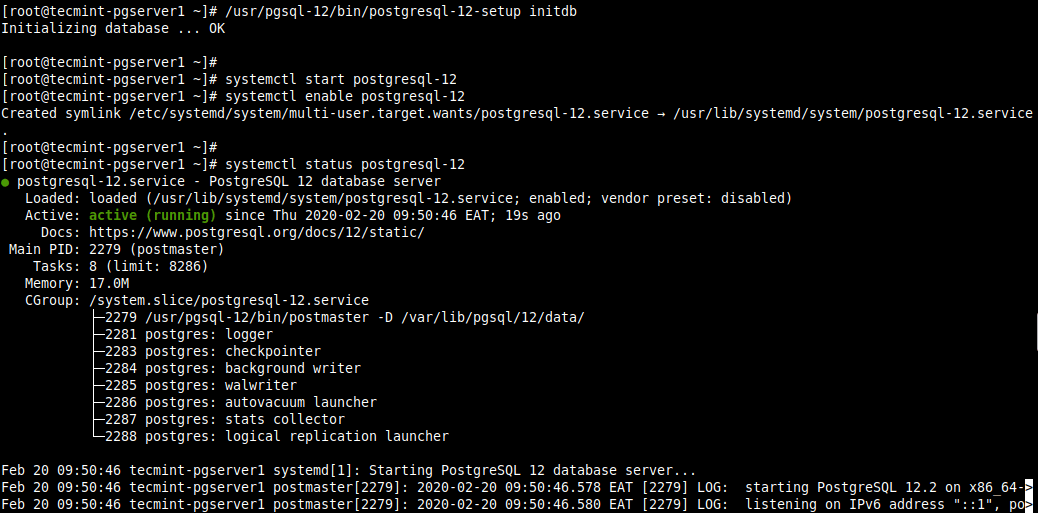
4. Once the installation is complete, initialize the PostgreSQL database, then start the PostgreSQL-12 service and enable it to automatically start at system boot. Then check if the service is up and running, and is enabled as shown.
# /usr/pgsql-12/bin/postgresql-12-setup initdb # systemctl start postgresql-12 # systemctl enable postgresql-12 # systemctl status postgresql-12 # systemctl is-enabled postgresql-12
Step 2: Secure and Configure PostgreSQL Database
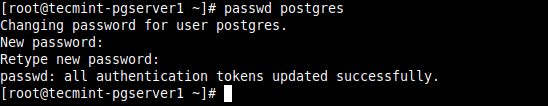
5. Next, secure the Postgres user account and the database administrative user account. Start by creating a password for a Postgres system user account using the passwd utility as shown.
# passwd postgres
6. Then switch to the Postgres system account and create a secure and strong password for PostgreSQL administrative database user/role as follows.
# su - postgres $ psql -c "ALTER USER postgres WITH PASSWORD '[email protected]';" $ exit

7. Now configure how the Postgres server will authenticate clients such as pgAdmin. The supported authentication methods include password-based authentication which uses one of these methods: md5, crypt, or password.
For this guide, we will configure md5 authentication method in the file /var/lib/pgsql/12/data/pg_hba.conf.
# vi /var/lib/pgsql/12/data/pg_hba.conf
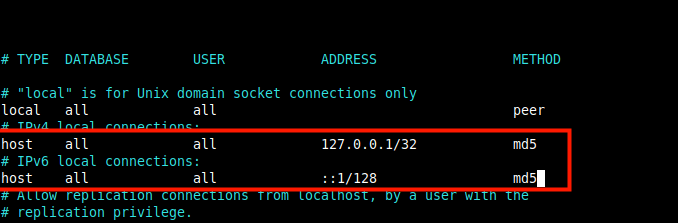
Find the following lines and change the authentication method to md5 as highlighted in the screenshot.
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 md5 host all all ::1/128 md5
8. After saving the file, to apply the recent changes in the Postgres configuration, restart the Postgres service.
# systemctl restart postgresql-12
Step 3: Installing pgAdmin4 in CentOS 8
9. Now we will install pgAdmin 4 to manage the PostgreSQL database from the web. First, you need to enable the EPEL and pgAdmin Yum repositories which contain some of the dependencies.
# dnf install epel-release # dnf install -y https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/pgadmin/pgadmin4/yum/pgadmin4-redhat-repo-1-1.noarch.rpm
on Fedora Linux, run:
# dnf install -y https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/pgadmin/pgadmin4/yum/pgadmin4-fedora-repo-1-1.noarch.rpm
10. Next, you need to remove PostgreSQL official yum repositories in order to install the latest stable version of pgAdmin from pgAdmin official yum repository.
# dnf remove -y pgdg-redhat-repo
11. Now build cache for newly installed pgAdmin and EPEL repositories and install pgAdmin using the following commands.
# dnf makecache # yum install pgadmin4
12. Next, start the httpd service and enable it to auto-start at system boot, then check if it is up and running as shown.
# systemctl start httpd # systemctl enable httpd # systemctl status httpd
Step 4: Configuring pgAdmin 4 in CentOS 8
13. The pgadmin4 package comes with a configurable script to configure the pgAdmin web service, which will create a user account used to authenticate in the web interface, configure SELinux policies and Apache webserver to deploy pgAdmin web service.
# /usr/pgadmin4/bin/setup-web.sh
Sample Output
Setting up pgAdmin 4 in web mode on a Redhat-based platform... Creating configuration database... NOTE: Configuring authentication for SERVER mode. Enter the email address and password to use for the initial pgAdmin user account: Email address: [email protected] Password: Retype password: pgAdmin 4 - Application Initialisation ====================================== Creating storage and log directories... Configuring SELinux... The Apache web server is running and must be restarted for the pgAdmin 4 installation to complete. Continue (y/n)? y Apache successfully restarted. You can now start using pgAdmin 4 in web mode at http://127.0.0.1/pgadmin4
14. If you have the firewalld service enabled and running, open ports 80 and 443 in the firewall to allow traffic to the HTTPD web server as shown.
# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone public --add-port 80/tcp # firewall-cmd --permanent --zone public --add-port 443/tcp # firewall-cmd --reload
Step 5: Accessing pgAdmin Web Interface
15. To access the pgAdmin web interface, open a browser and navigate using the following URL.
http://SERVER_IP/pgadmin4 OR http://localhost/pgadmin4
Once the login interface loads, use the email address and password you created in step 15 above to log in.
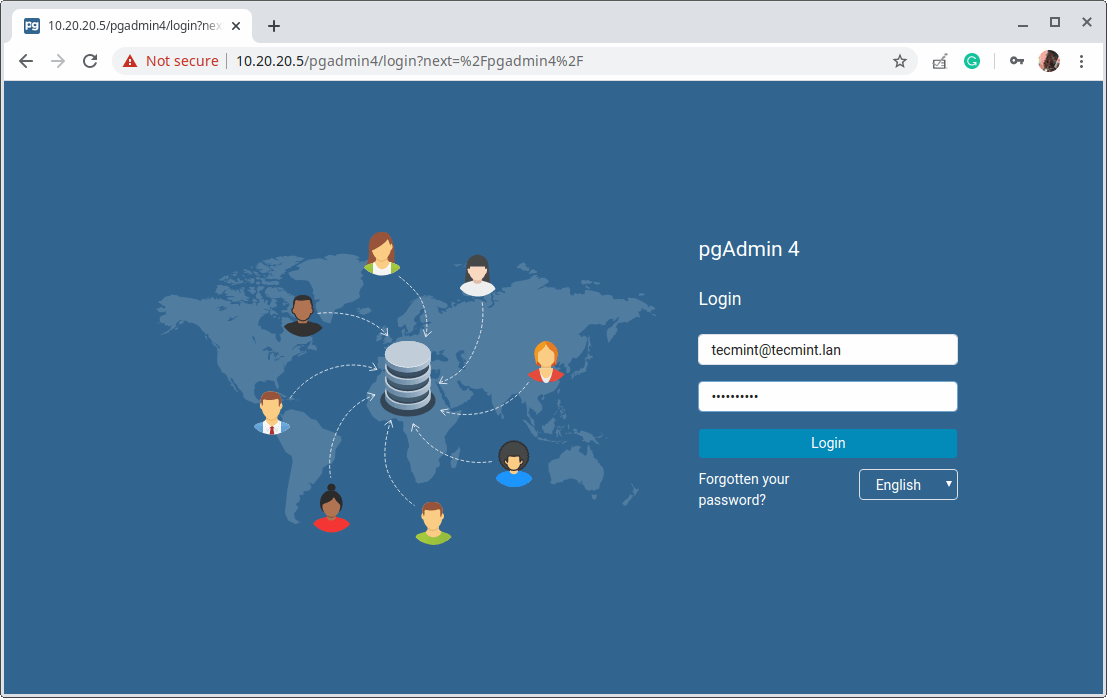
16. Next, add a new server connection by clicking on “Add New Server”.
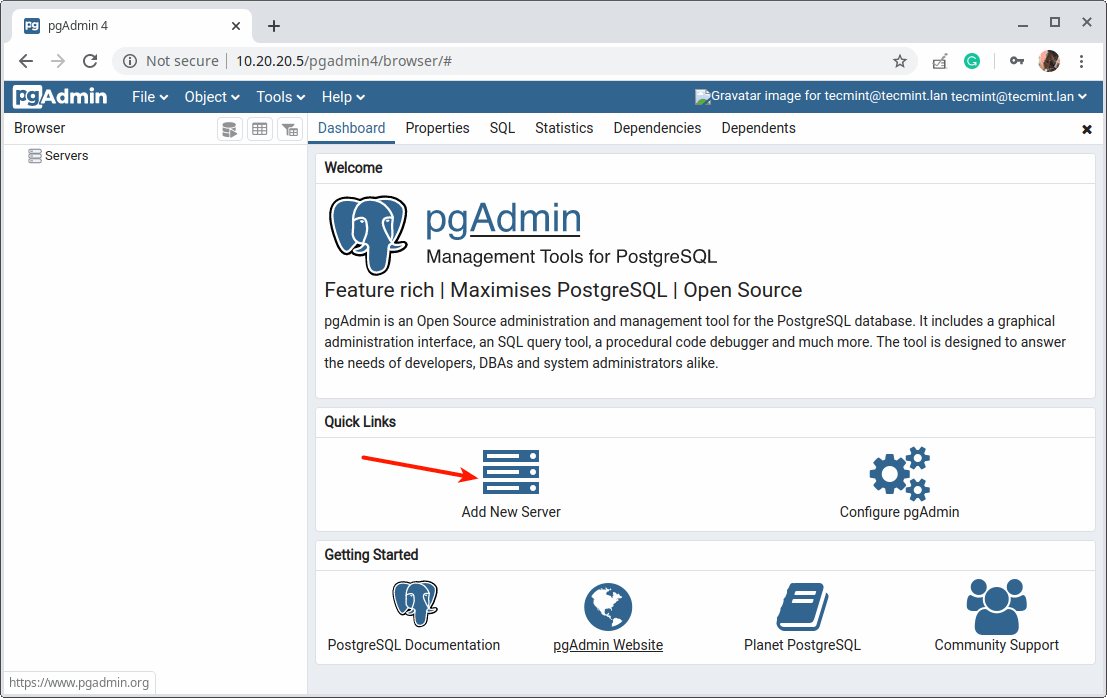
17. Then under the “General” tab, enter the following settings server Name and optionally leave a comment to describe the connection.
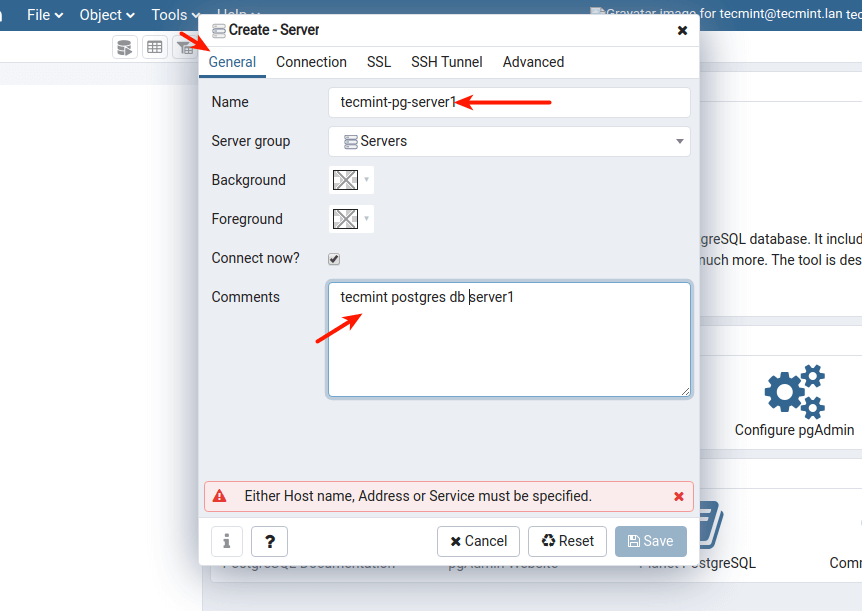
18. Then define the connection profile by filling in the following:
- Host – host/IP address of the PostgreSQL server.
- Port – defaults to 5432.
- Maintenance Database – defaults should be Postgres.
- Username – the database username. You can use Postgres.
- Password – password for the above user.
Then click Save.
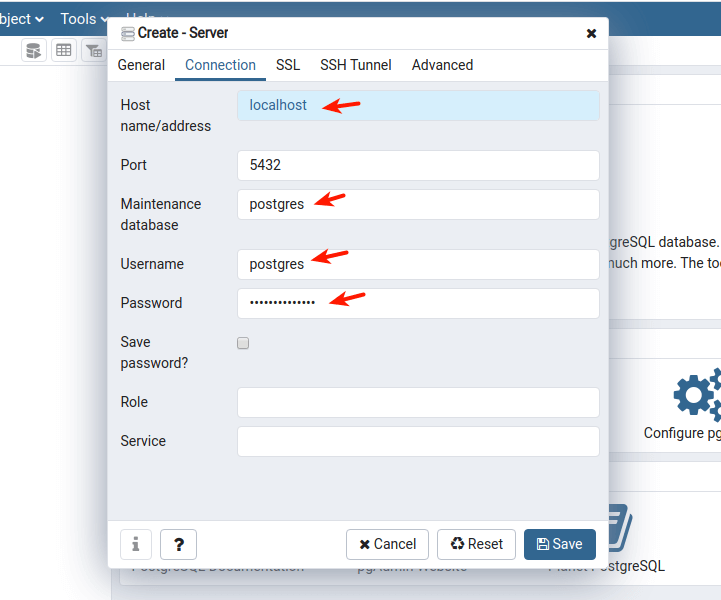
19. The new server should now appear under the list of servers as highlighted in the following screenshot.
20. When you click on the server name, its attributes should load under the Dashboard as shown in the following screenshot.
There you have it! You have successfully installed Postgresql 12 and pgAdmin 4 in CentOS 8. Reach us via the feedback form below for any thoughts and questions. You can find more information in the Postgresql 12 documentation and pgAdmin documentation.