In this post, we will learn a number of commands for locating the default configuration files for MySQL database server (my.conf), PHP programming language (php.ini) and Apache HTTP server (http.conf), which together with Linux form the LAMP (Linux Apache Mysql/MariaDB PHP) stack.
A configuration file (or config file) contains system related or application settings. It gives developers and administrators control over operation of the system or an application.
As a Linux Sysadmin, knowing the location of configuration files or mastering means of finding them is an invaluable skill.
In Linux Directory Structure, the /etc directory or its sub-directories store system related or application configuration files.
Although this is the primary location of configuration files, a few developers choose to store other configuration files in custom directories.
How To Find MySQL (my.conf) Configuration File
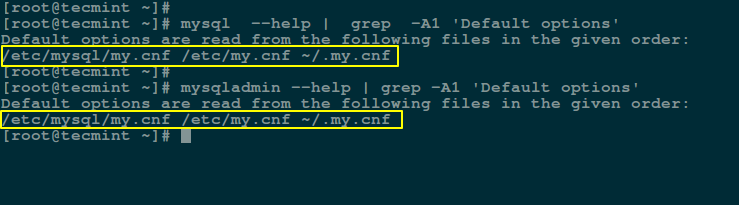
You can locate the the MySQL configuration file using the mysql command line tool or mysqladmin, a client for managing a MySQL server.
The following commands will display the mysql or mysqladmin help page, which includes a section that talks about the files (configuration files) from which default options are read.
In the commands below, the grep option -A displays NUM lines of trailing context after matching lines.
$ mysql --help | grep -A1 'Default options' OR $ mysqladmin --help | grep -A1 'Default options'
Make an effort to master the MySQL administration through these helpful articles.
- Learn MySQL for Beginners Guide – Part 1
- Learn MySQL for Beginners Guide – Part 2
- 20 Useful Mysqladmin Commands for Database Administration
How To Find PHP (php.ini) Configuration File
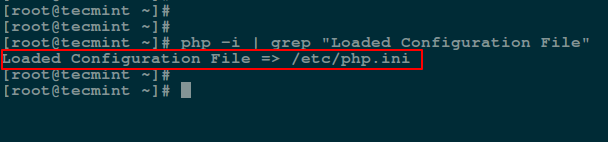
PHP can be controlled from the terminal using php command line utility, in conjunction with the -i switch which enables showing of PHP information and configurations and grep command help you to can find the PHP configuration file like so:
$ php -i | grep "Loaded Configuration File"
Find Apache http.conf/apache2.conf Configuration File
You can invoke apache2 directly (which is not recommended in most cases) or administer it using apache2ctl control interface as below with the -V flag which shows the version and build parameters of apache2:
--------- On CentOS/RHEL/Fedora --------- $ apachectl -V | grep SERVER_CONFIG_FILE --------- On Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint --------- $ apache2ctl -V | grep SERVER_CONFIG_FILE

That’s all! Remember to share your thoughts about this post or provide us other possible ways of locating the above configuration files in the comments.



